Peking University, Nov. 16, 2010: An anti-cancer research jointly conducted by The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) and Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School (PKUSZ) has led to the first total synthesis of an anti-cancer marine natural product, grassypeptolide.

Not only was this important finding featured on the inside front cover of the journal Chemical Communications (Issue 40, Volume 46, 2010), but also highlighted by Nature China .
This cutting-edge research has combined the effort of two research teams from PolyU and PKUSZ, both working under the leadership of Principal Investigator Dr. Ye Tao, Associate Professor of PolyU’s Department of Applied Biology and Chemical Technology, and of PKUSZ Laboratory of Chemical Genomics.
The team also includes Liu Hui, Xing Xiangyou, and Xu Zhengshuang from PKUSZ.

Prof. Ye Tao
This breakthrough has paved the way for further development of anti-cancer drugs from this natural product grassypeptolide – a compound isolated from a marine bacteria – which has recently emerged as a promising anti-cancer agent.
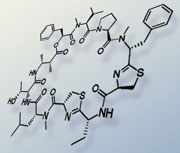
Grassypeptolide
Despite its fascinating features, grassypeptolide was barely available from natural sources. But now it can be constructed by total chemical synthesis in 17 steps with this breakthrough. The key challenges in the total synthesis of grassypeptolide are the forming of the 31-member ring of grassypeptolide and the introducing of the two smaller thiazoline heterocycles – five-member rings containing sulphur and nitrogen – into the 31-member ring. The researchers constructed the 31-membered macrocycle via a precursor with more favorable cyclization kinetics; and introduced the thiazoline heterocycles at a later stage of the synthesis to prevent the thiazoline heterocycles from undergoing side reactions.
According to Dr. Ye, chemical synthesis of natural products and their analogues has been a key tool for drug discovery and development. In cases where the lead compound is obtainable only in minute quantities, thus not enough to carry out further bioassay tests, chemical synthesis can solve the supply problem. Furthermore, the synthesis presents opportunities for modifying the structure of lead compound, with the ultimate aim of improving activity or the physicochemical/biological properties of the lead molecule. Synthesis is also crucial in the development of structure-activity relationships as the ability to make analogues of the lead compound chemically is a prerequisite for such studies.
Edited by: Jacques
Source: Hong Kong Polytechnic University