Peking University, December 13, 2018: On December 6, Biological Psychiatry, a world-leading academic journal(IF=18.982), published the collaborative findings written by Huang Zhuo research team from PKU State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, and Liang Jing research team from PKU School of Basic Medical Sciences. The paper is titled “CDYL-mediated histone crotonylation regulates stress-induced depressive behaviors”.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent and life-threatening illness in modern society. The susceptibility to MDD is profoundly influenced by environmental factors, such as stressful lifestyle or traumatic events, which could impose maladaptive transcriptional program through epigenetic regulation. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. Huang Zhuo’s and Liang Jing’s research teams examined the role of histone crotonylation (Kcr), a novel type of histone modification, and chromodomain Y-like (CDYL), a crotonyl-CoA hydratase and histone methyllysine reader, in this process. For the first time, their results demonstrate that CDYL-mediated histone crotonylation plays a critical role in regulating stress-induced depression, providing a potential therapeutic target for MDD.
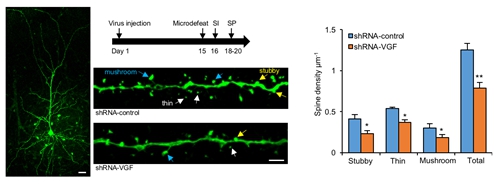
Lowering VGF can apparently reduce the number of dendritic spine in PL encephalic region
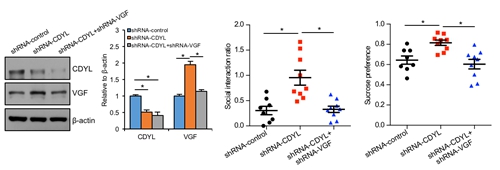
CDYL affects the depression of rats through adjusting the expression of VGF
The research is funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation.
Written by: Wang Xi
Edited by: Huang Yadan
Source: PKU News (Chinese)

